Anodizing processes play an important role in improving both the performance and appearance of metal components. From aerospace to automotive, electronics to construction, anodizing has become a standard method for increasing durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic value. In this blog by Asian Coater, we’ll explain what the anodizing process is, why it is used, how it works, and the step-by-step procedures involved in anodizing.
What is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. Unlike other coating processes that apply a material on top of the surface, anodizing modifies the surface itself, making it an integral and durable layer of the metal.
This process is most commonly used on aluminum, though other non-ferrous metals like titanium and magnesium can also be anodized. The anodic oxide layer is porous, which means it can also absorb dyes and other sealants, giving manufacturers a wide range of color and finish options.
Why are Anodizing Processes Important?
The anodizing processes offer numerous functional and decorative benefits:
- Corrosion Resistance: The oxide layer protects the metal from environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation.
- Increased Surface Hardness: Makes the surface more resistant to wear and abrasion.
- Enhanced Adhesion: The porous surface allows for better adhesion of paints, sealants, and lubricants.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Anodizing allows for a range of vibrant, long-lasting colors without peeling or fading.
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike plating and painting, anodizing doesn’t release harmful solvents and produces minimal waste.
Anodizing Process Steps
The anodizing process steps are vital to grasp how this technique works and what makes it so effective. Here’s a breakdown of the standard steps involved in anodizing aluminum:
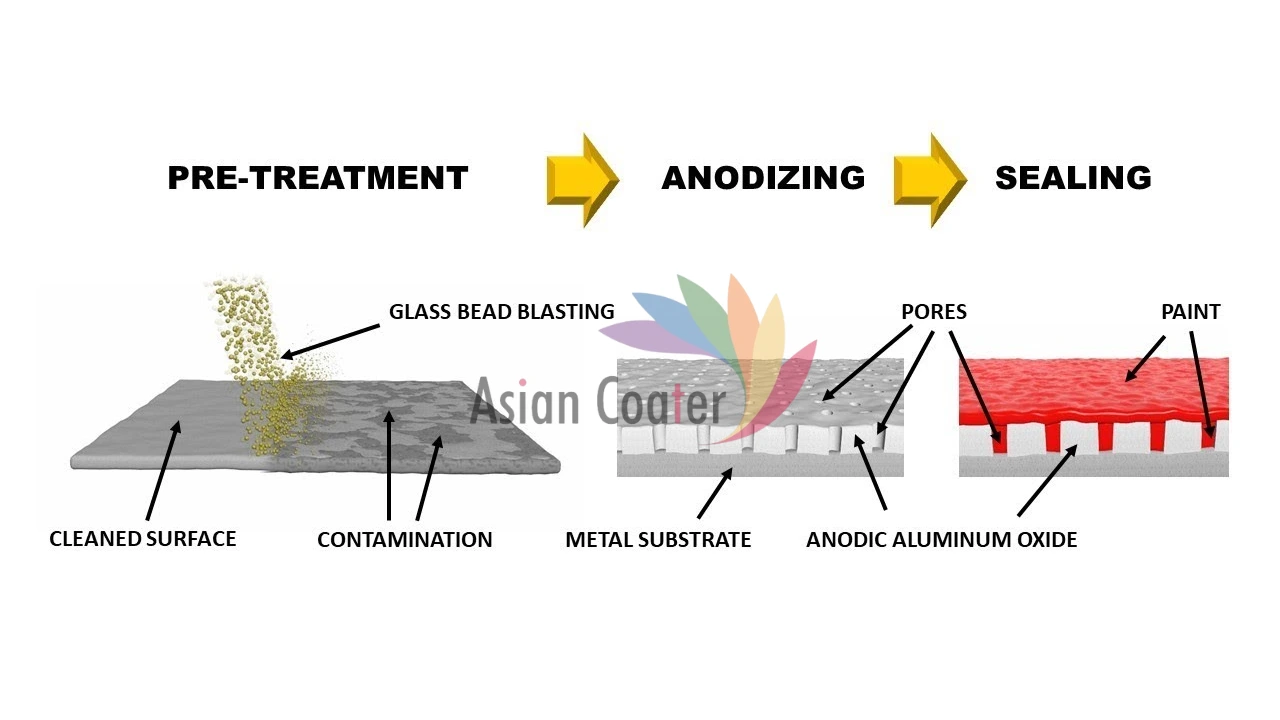
- Pre-Treatment (Cleaning & Etching) – Before anodizing can begin, the metal surface must be perfectly clean and free of contaminants like grease, dirt, or oxide scales.
- Desmutting – After etching, the surface may have a residue known as “smut” (metallic residues). Desmutting involves treating the part with an acid solution (like nitric acid) to remove these residues and prepare the surface for uniform anodizing.
- Anodizing (Electrochemical Conversion) – This is the core step of all anodizing processes. The cleaned and pre-treated metal is submerged in an electrolytic solution, usually sulfuric acid, and connected to the positive terminal (anode) of a DC power source.
- Coloring (Optional) – One of the unique advantages of anodizing is the ability to add color. This is done after anodizing but before sealing:
- Electrolytic Coloring: Involves immersing the anodized part in a bath containing metal salts to produce metallic shades like bronze or black.
- Organic Dyeing: The porous surface can absorb organic dyes, giving vibrant color options like red, blue, green, and gold.
- Sealing – Once the desired finish is achieved, the pores of the anodized layer are sealed to enhance corrosion resistance and color fastness.
Types of Anodizing Processes
There are different anodizing processes depending on the application, desired appearance, and metal type. The most common include: Chromic Acid Anodizing, Sulfuric Acid Anodizing, Hardcoat Anodizing.
Applications of Anodizing
- Automotive: Trim, wheels, engine parts
- Aerospace: Structural components, cockpit instruments
- Architecture: Window frames, curtain walls, handrails
- Consumer Goods: Smartphones, laptops, kitchenware
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, housings
Maintenance of Anodized Surfaces
Anodized surfaces are easy to maintain, but proper care ensures they last even longer: Use mild soap and water for cleaning, Avoid abrasive scrubbers that may scratch the surface, For architectural applications, periodic cleaning prevents discoloration.
Conclusion
Anodizing is more than just a surface treatment—it’s a high-performance, eco-friendly, and cost-effective way to improve the life and look of metal parts. With increasing demand for durability and design flexibility, anodizing processes continue to dominate various manufacturing sectors. From pre-treatment to sealing, each of the anodizing process steps plays a vital role in delivering a finish that’s as functional as it is beautiful.
Asian Coater specialize in advanced surface finishing solutions and are proud to support industries with top-tier anodizing and coating technologies. Whether you’re looking for decorative aluminum anodizing or hard coat finishes for extreme environments, we’re here to deliver quality and consistency.